Mental health definition.
A person's mental health refers to their overall psychological well-being. It entails being able to control one's emotions, thoughts, and behaviors. A positive mental health is essential for overall health and happiness. It can assist a person in leading a fulfilling and productive life as well as contributing to their community.
Poor mental health, on the other hand, can cause a variety of problems and difficulties, including difficulties in relationships, difficulties functioning at work or school, and even physical health issues.
Genetics, life experiences, and environmental factors can all have an impact on one's mental health. It is critical to monitor one's mental health and seek help if necessary.
What is mental health?
The term "mental health" refers to a person's overall emotional, psychological, and social well-being. It is an important aspect of overall health that can be influenced by a number of factors such as life events, genetics, and environmental factors. Mental health is more than just the absence of mental health disorders; it is also the presence of positive characteristics and coping skills that allow a person to navigate life's challenges and contribute meaningfully to their community.
10 reasons why mental health is important
1. Mental health allows you to deal with life's ups and downs: Good mental health allows you to deal with life's ups and downs. It enables you to recover from adversity and learn from difficult experiences.
2. Mental health improves physical health: A strong link exists between mental and physical health. Chronic stress, for example, can wreak havoc on the immune system and increase the risk of physical health issues like heart disease and diabetes.
3. Improves your quality of life: Good mental health allows you to enjoy your life and the people in it. It makes you feel good about yourself and gives you a positive outlook on life.
4. Mental health influences success: People who have good mental health are more likely to succeed in their studies, work, and personal relationships. They can concentrate better, make better decisions, and solve problems.
5. Relationships require good mental health: Good mental health is required for developing and maintaining strong, healthy relationships. It allows you to communicate effectively, demonstrate empathy, and resolve conflicts in a healthy manner.
6. Mental health promotes resilience: Having good mental health allows you to recover from setbacks and persevere in the face of difficulties. It aids in the development of resilience, or the ability to adapt and recover from adversity.
7. Mental health is a human right: Everyone has the right to good mental health. Everyone, regardless of income, race, or ethnicity, should have access to mental health care and support.
8. Mental health is critical to social justice: Marginalized and disadvantaged groups are disproportionately affected by poor mental health. Taking care of one's mental health is an important part of promoting social justice and reducing inequalities.
9. Mental health is essential at all stages of life: Mental health is essential for people of all ages, from children to the elderly. It is critical to prioritise mental health throughout one's life and to seek help when necessary.
10. Everyone is responsible for mental health: We all have a role to play in promoting mental health and supporting those who are struggling. This entails looking after our own mental health as well as helping out friends, family, and those in the community who might be in need.
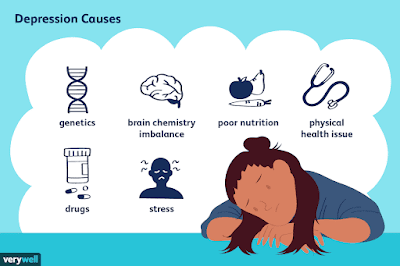
1. Risk factors for mental health conditions
There are many different risk factors that can increase the likelihood of developing a mental health condition. Some of the most common risk factors include:
Genetics
Life experiences
Environmental factors
Substance abuse
Physical health problems
Social isolation
Stress
Family history
Continuous social and economic pressure
Continuous social and economic pressure can have a negative impact on one's mental health. Work, financial difficulties, and social isolation are all examples of sources of this type of stress.
Work pressure: Long hours, demanding job responsibilities, and a lack of work-life balance can all contribute to stress and burnout, which can have a negative impact on mental health.
Financial difficulties: Struggling to make ends meet, dealing with debt, or worrying about financial security are all sources of stress that can have a negative impact on mental health.
Social isolation: A lack of strong social connections and support can lead to feelings of loneliness and isolation, which can have a negative impact on mental health.
Constant social and economic pressures can lead to mental health issues such as anxiety, depression, and burnout.It is important to be aware of the potential impacts of these pressures and to seek support if needed.
Childhood adversity
Childhood adversity refers to negative childhood experiences or exposures such as abuse, neglect, household dysfunction, or exposure to violence. These kinds of experiences can have serious consequences for a child's physical, emotional, and mental health.
Adversity may put children at risk for a variety of mental health issues, including anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). They may also be predisposed to physical health issues such as obesity, heart disease, and diabetes.
Biological factors
Biological factors are factors that are related to a person's physical body and how it functions. There are many different biological factors that can affect mental health, including:
Genetics: Certain mental health conditions, such as depression and schizophrenia, can run in families, suggesting that there may be a genetic component to these conditions.
Brain chemistry: Abnormalities in brain chemistry, such as imbalances in neurotransmitters, can affect mental health.
Hormones: Hormonal imbalances, such as those that occur during menopause or after childbirth, can affect mental health.
Medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as chronic pain or a thyroid disorder, can affect mental health.
Substance use: Substance abuse, including alcohol and drug use, can affect mental health.
Sleep: Lack of sleep or poor sleep quality can affect mental health.
Biological factors can play a role in the development and treatment of mental health conditions. For example, certain medications that affect brain chemistry can be used to treat mental health conditions such as depression and anxiety.
2. Types of mental health disorders
There are many different types of mental health disorders, ranging from common disorders such as depression and anxiety to more rare disorders such as schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Some common types of mental health disorders include:
Anxiety disorders
Mood disorders
Psychotic disorders
Anxiety disorders
Anxiety disorders are a type of mental health disorder characterized by excessive worry or fear that is out of proportion to the situation. These feelings can interfere with a person's ability to function in daily life.
Generalized anxiety disorder
Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) is a type of anxiety disorder characterized by excessive, persistent worry about a variety of topics, such as work, health, or relationships. The worry is often not tied to any specific event or situation and can be difficult to control.
- Panic disorder
Panic disorder is a type of anxiety disorder characterized by sudden, intense episodes of fear or panic that can come on without warning. These episodes, called panic attacks, are often accompanied by physical symptoms such as heart palpitations, shortness of breath, and dizziness.
- Mood disorders
Affective disorders, commonly referred to as mood disorders, are a subset of mental health conditions marked by ongoing fluctuations in mood that impair one's capacity to carry out daily activities. Depression and bipolar illness are the two most typical forms of mood disorders.
Depression is a mental health condition characterised by persistent depressive thoughts, a sense of helplessness, and a lack of interest in routinely enjoyable pursuits. Changes in sleep and eating patterns, difficulties focusing, and thoughts of suicide or death are some further signs of depression.
A mental health condition known as bipolar disorder is characterised by episodes of extremely high or low moods (depression). These episodes might linger for several days or even weeks, interfering with a person's ability to carry out daily tasks.
- Schizophrenia disorders
Schizophrenia is a serious mental illness that has an impact on a person's thoughts, feelings, and actions. It is a chronic condition that often appears in late adolescence or the beginning of adulthood.
Although it can be difficult to manage, schizophrenia is a treatable disorder. Antipsychotic drugs and counselling, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy or family therapy, are frequently used in treatment.
3. Early signs
It can be difficult to identify the early signs of mental health disorders, as they can vary widely and may be different for each person. Some common early signs of mental health problems can include:
Changes in mood
Changes in behavior
Changes in thinking and perception
Changes in physical health
4. Treatment
There are many different treatment options available for mental health disorders, and the most effective treatment plan will depend on the individual and the specific mental health disorder they are experiencing. Some common treatment options include:
Therapy: Therapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy, can help individuals to identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to mental health problems.
Medication: Medications, such as antidepressants or antipsychotics, can help to reduce symptoms of mental health disorders.
Self-care: Engaging in activities that promote physical and emotional well-being, such as exercise, getting enough sleep, and eating a healthy diet, can help to improve mental health.
Support from loved ones: Support from friends and family can be an important part of treatment for mental health disorders.
Complementary and alternative treatments: Some people find relief from mental health symptoms through complementary and alternative treatments, such as meditation, acupuncture, or herbal remedies.
It is important to work with a mental health professional to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for a specific mental health disorder. With appropriate treatment, it is possible to manage mental health disorders and improve quality of life.
Psychotherapy, or talking therapies
Talking with a qualified mental health professional is a key component of psychotherapy, commonly referred to as talking therapy or counselling, which is a method of treatment for mental health illnesses. Psychotherapy can be a useful treatment for a variety of mental health conditions, including depression, anxiety, and bipolar disorder. It can also help people understand and regulate their thoughts, feelings, and actions.
- Medication
Medication can be an effective treatment for many mental health disorders, including depression, anxiety, and psychotic disorders such as schizophrenia.There are many different types of medications used to treat mental health disorders, including:
Antidepressants: Antidepressants are medications that are used to treat depression and some anxiety disorders. There are several different types of antidepressants, including selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), and tricyclic antidepressants.
Antipsychotics: Antipsychotics are medications that are used to treat psychotic disorders such as schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder. They can help to reduce symptoms such as delusions and hallucinations.
5. How to maintain your mental health
There are many things that individuals can do to maintain their mental health and well-being. Some strategies that may be helpful include:
Getting enough sleep: Getting enough sleep is important for physical and mental health. It is recommended that adults aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night.
Eating a healthy diet: A diet that is rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains and that is low in processed foods can support good mental health.
Staying physically active: Regular physical activity has been shown to improve mood and reduce stress.
Connecting with others: Strong social connections are important for mental health. Make time for activities that involve interacting with others, such as hobbies or sports.
Managing stress: Find healthy ways to manage stress, such as through exercise, meditation, or talking to a mental health professional.
Seeking help when needed: Don't be afraid to seek help from a mental health professional if you are struggling with your mental health. Early treatment can often be more effective in managing mental health problems.
It is also important to be aware of warning signs of mental health problems and to seek help if needed. These can include changes in mood, changes in behavior, and difficulties functioning in daily life.
6. Suicide prevention
Suicide is a serious and preventable public health issue. It is important to be aware of the warning signs of suicide and to know how to help someone who may be considering suicide.
Warning signs of suicide can include:
1. Talking about wanting to die or kill oneself
2. Expressing feelings of hopelessness or having no reason to live
3. Talking about feeling trapped or in unbearable pain
4. Increasing the use of alcohol or drugs
5. Acting anxious or agitated
6. Withdrawing from friends and family
7. Changing eating and sleeping habits
8. Giving away belongings
9. Saying goodbye to people
If you are concerned that someone may be considering suicide, it is important to take their words and behaviors seriously and to offer support and assistance. You can help by:
Asking directly about suicide: Asking someone if they are considering suicide can be difficult, but it is an important step in getting them the help they need.
Listening: Let the person know that you are there to listen and that they are not alone.
Connecting the person to resources: Help the person connect with a mental health professional or a support hotline.
Removing access to lethal means: If the person has access to firearms or other lethal means, it is important to remove them from the person's home to reduce the risk of suicide.
If you are struggling with thoughts of suicide, it is important to seek help from a mental health professional or a support hotline. You are not alone and there is help available.
Summary
A person's complete emotional, psychological, and social well-being is referred to as their mental health. It is a crucial component of overall health and is influenced by a number of things, including genetics, environmental variables, and life events. Mental health problems are conditions that can impair daily functioning by upsetting a person's thoughts, emotions, and behaviour.
Mental health disorders come in a wide variety of forms, such as eating disorders, substance abuse disorders, psychotic disorders, psychotic disorders, psychotic disorders, psychotic disorders, and personality disorders. Disorders of the mind can cause a wide range of symptoms, such as mood swings, behavioural abnormalities, and problems carrying out regular tasks.